
Ensuring Your DSPM Tool Is
As Effective As Possible
Author: Ben Norcutt
Release Date: 08/10/2025
What is DSPM?
You may have heard the term or even its predecessor SSPM so lets define what they actually are first.
SSPM - SaaS Security Posture Management, an acronym within an acronym but basically it’s looking at the configuration of a cloud service like SalesForce CRM or Box to ensure that it meets regulatory and cyber security standards.
DSPM - Data Security Posture Management, again it’s looking at the configuration to make sure it meets regulatory and cybersecurity standards but it’s also layering on awareness of the sensitivity of the data residing in these environments. Traditional SaaS Security Posture Management tools were limited to just SaaS products but Securiti DSPM manages any cloud based service. This includes IaaS such as AWS S3 buckets, PaaS like Azure SQL whilst still able to work with SaaS products.
For example:
Amazon S3 bucket shared publicly contains public price list = GOOD
Amazon S3 bucket publicly contains M&A data = BAD
So now we know what DSPM is. How do we implement DSPM into our daily life?
Introduction
Implementing a DSPM tool is a strategic decision that requires a solid foundation in data governance.
By establishing the following prerequisites, organisations can ensure that their DSPM tool is effective in protecting sensitive data, maintaining compliance, and enhancing overall data security posture.
Proper data governance not only facilitates the implementation of DSPM tools but also strengthens the organisation’s ability to manage and secure its data assets in the long term.
Here are the key data governance prerequisites for implementing a DSPM tool:
1. Data Discovery and Classification
Inventory: A comprehensive inventory of all data assets is crucial. This inventory should include data sources, types, storage locations, and data flows within the organisation.
Classification: All data should be classified and labelled based on sensitivity and importance. Common classifications and labels include public, internal, confidential, and highly confidential. This classification helps in applying appropriate security controls and policies.

2. Data Ownership and Accountability
Ownership: Clearly define data ownership. Every data asset should have an assigned owner responsible for its security, integrity, and accessibility.
Accountability: Establish clear lines of accountability for data management. This includes roles and responsibilities for data stewards, custodians, and users.
3. Data Policies and Standards
Policies: Develop and implement robust data security policies that outline acceptable use, access controls, data sharing, and data retention practices.
Standards: Create data handling and protection standards that align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements. These standards should undergo regular review and be updated accordingly.
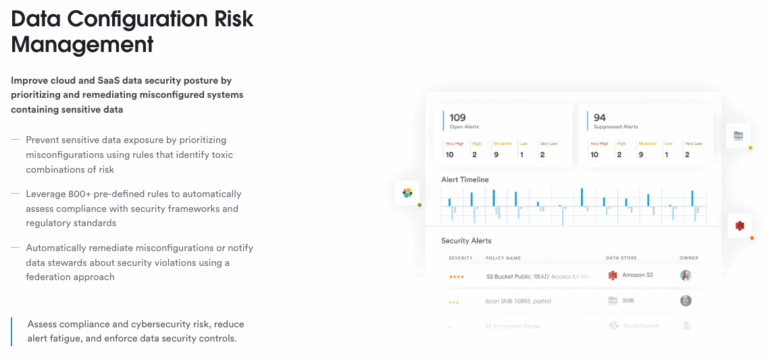
4. Data Access Controls
Access Management: Implement stringent access controls based on the principle of least privilege. Ensure that only authorised users have access to sensitive data.
Authentication and Authorisation:Automatically enforce policy- based access controls and apply dynamic masking of sensitive data based on attributes.
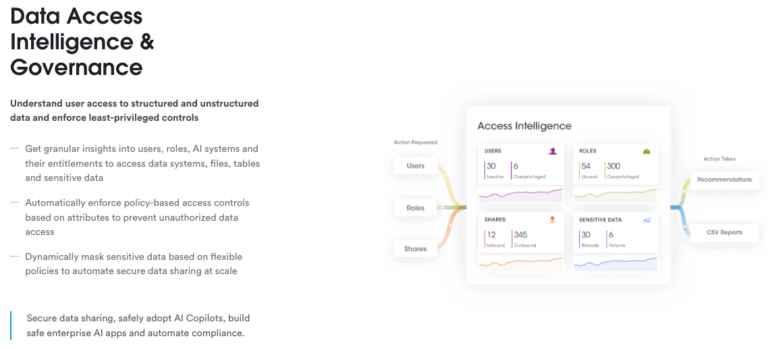
5. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory Alignment: Ensure that your data governance framework complies with relevant laws and regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA etc. This includes understanding data residency and data transfer requirements.
Auditing: Implement regular auditing and monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance and to identify potential gaps in data governance practices.
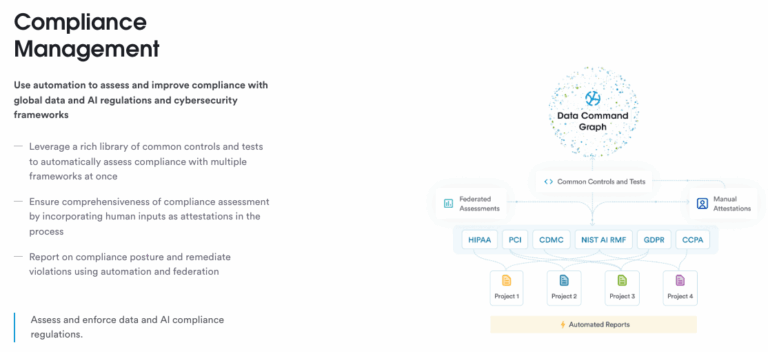
6. Data Lifecycle Management
Retention Policies: Establish data retention policies that comply with regulatory requirements and business needs. These policies should be automated where possible to ensure consistency.

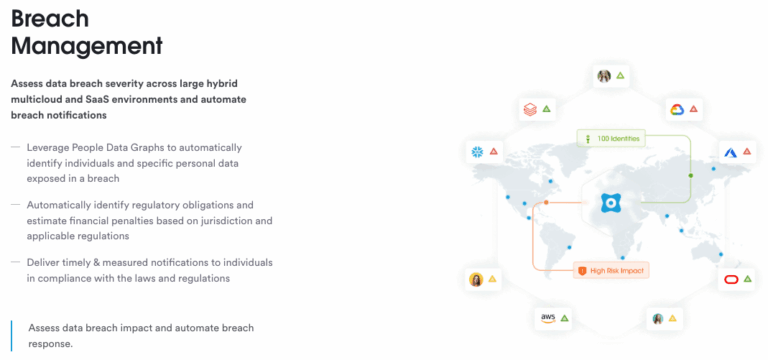
7. Incident Response and Data Breach Management
Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that includes procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from data breaches.
Breach Notification: Establish protocols for breach notification in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. This includes internal and external communication plans.
8. Training and Awareness
Training Programs: Implement regular training and awareness programs for employees to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities in data governance and data security. Security also offers free DSPM training for anyone to get started with at https://education.securiti.ai/certifications/dspm/
Culture of Security: Foster a culture of security within the organisation where data protection is everyone’s responsibility.

9. Technology Integration and Interoperability
Integration: Ensure that the DSPM tool can integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure, including data lakes, databases, and other security tools.
Interoperability: The DSPM tool should be able to work with other security and monitoring tools to provide a comprehensive view of the organisation's data security posture.

Securiti is an AI-powered platform for data security and compliance. We are delighted to partner with this renowned organisation to offer the seamless deployment of DSPM tools. If you’re interested in learning more about Securiti’s solutions, and about our technology partnership, you can visit our partner page or our events page!

